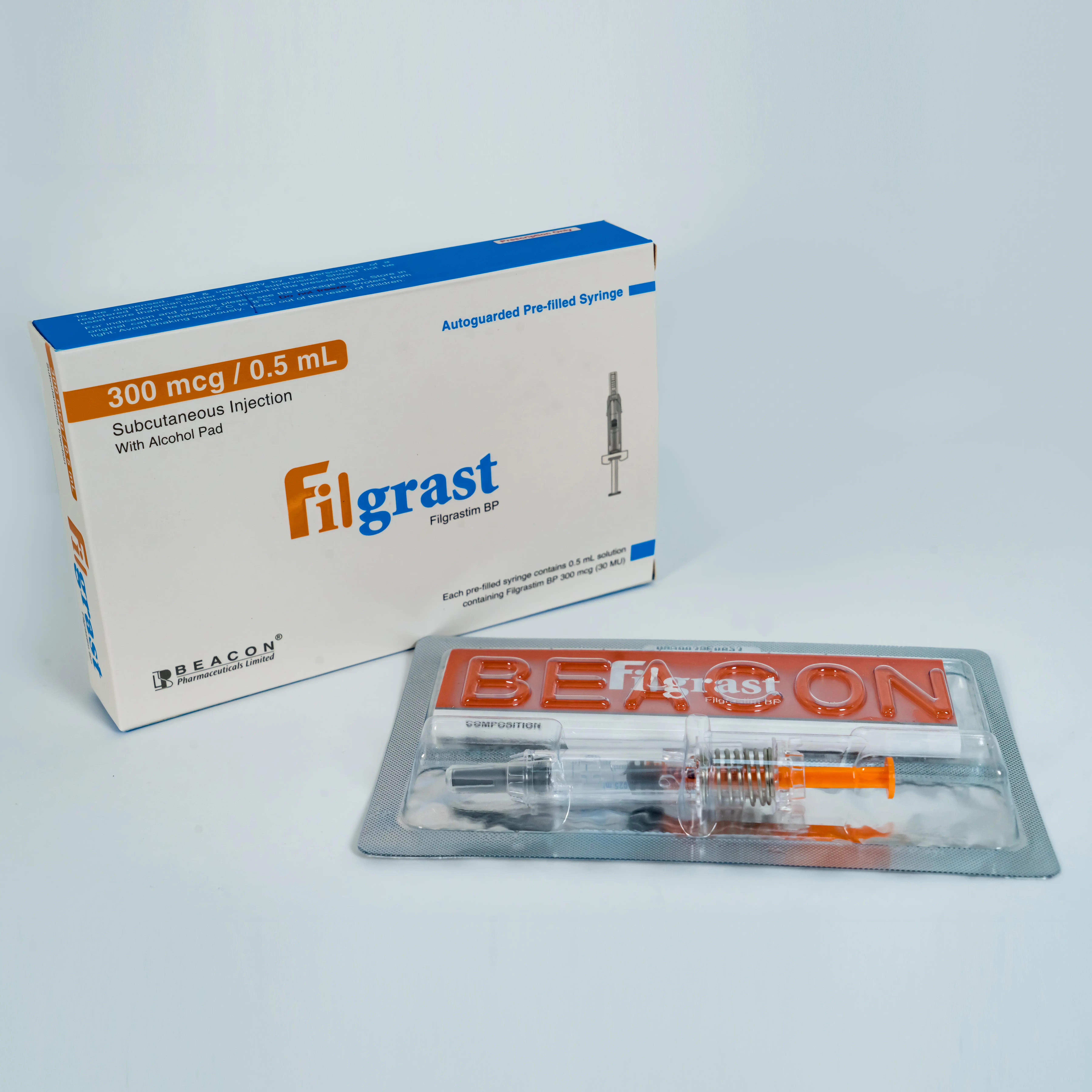
0.5 ml pre-filled syringe:
৳ 2,500.00
Indications
Cancer patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy: The decrease of the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with non myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with a significant incidence of severe neutropenia with fever.
Cancer patients undergoing Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The reduction of the time to neutrophil recovery and the duration of fever, following induction or consolidation chemotherapy treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Cancer Patients Receiving Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT): The reduction of the duration of neutropenia and neutropenia-related clinical sequelae, e.g., febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablatlve chemotherapy followed by bone marrow transplantation.
Patients with severe chronic neutropenia: The reduction of the incidence and duration of sequelae of neutropenia (e.g., fever, infection or opharyngeal ulcers) in symptomatic patients with congenital neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia or idiopathic neutropenia.
Patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation: The increase of the survival in patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation (Hematopoietic syndrome of acute radiation syndrome).
Patients with HIV infection: The prevention and treatment of persistent neutropenia in patients with advanced HIV infection, in order to reduce the risk of bacterial infections, when other options to manage neutropenia are inappropriate.
Cancer patients undergoing Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The reduction of the time to neutrophil recovery and the duration of fever, following induction or consolidation chemotherapy treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Cancer Patients Receiving Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT): The reduction of the duration of neutropenia and neutropenia-related clinical sequelae, e.g., febrile neutropenia, in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablatlve chemotherapy followed by bone marrow transplantation.
Patients with severe chronic neutropenia: The reduction of the incidence and duration of sequelae of neutropenia (e.g., fever, infection or opharyngeal ulcers) in symptomatic patients with congenital neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia or idiopathic neutropenia.
Patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation: The increase of the survival in patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation (Hematopoietic syndrome of acute radiation syndrome).
Patients with HIV infection: The prevention and treatment of persistent neutropenia in patients with advanced HIV infection, in order to reduce the risk of bacterial infections, when other options to manage neutropenia are inappropriate.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Pharmacology
Filgrastim is a 175 amino acid human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) manufactured by recombinant DNA technology. Filgrastim regulates the production of neutrophils within the bone marrow and affects neutrophil progenitor proliferation and differentiation. It also causes the enhanced phagocytic ability, priming of the cellular metabolism associated with respiratory burst, antibody-dependent killing and the increased expression of some cell surface antigens.
Filgrastim exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Clearance is dependent on Filgrastim concentration and neutrophil count. Filgrastim is cleared by kidney. It has a tmax of 2 to 8 hours. The absolute bioavailability of Filgrastim after subcutaneous administration is 60-70%.
Filgrastim exhibits nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Clearance is dependent on Filgrastim concentration and neutrophil count. Filgrastim is cleared by kidney. It has a tmax of 2 to 8 hours. The absolute bioavailability of Filgrastim after subcutaneous administration is 60-70%.
Dosage & Administration
Cancer patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or induction and/or consolidation chemotherapy for AML: The recommended dose of Filgrastim is 0.5 MU (5 mcg)/kg/day, administered as a single daily subcutaneous injection or by intravenous infusion (over 30 minutes). The first dose shouldn't be administered in less than 24 hours following cytotoxic Chemotherapy. Continue until neutrophil count in normal range, usually for 14 days (up to 38 days in AML.)
Cancer patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation: The recommended dosage of Filgrastim following bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg/day given as an intravenous infusion no longer than 24 hours. Administer the first dose of Filgrastim at least 24 hours after cytotoxic chemotherapy and at least 24 hours after bone marrow transplantation. Dose adjustment should be accordingly to absolute neutrophil count (ANC).
Patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell (PBPC) collection and therapy: The recommended dosage of Filgrastim for the mobilization of autologous PBPC is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg/day given by subcutaneous injection for 5-7 days. Administer Filgrastim for at least 4 days before the first leukapheresis procedure and continue until the last leukapheresis. Discontinue Filgrastim if the white blood cell (WBC) count rises to greater than 100,000/mm³.
Patients with severe chronic neutropenia: The recommended starting dosage in patients with congenital neutropenia is 0.6 MU (6 mcg)/kg as a twice daily subcutaneous injection and with idiopathic or cyclic neutropenia is 0.5 MU (5 mcg)/kg as a single daily subcutaneous injection. Dose adjustment should be accordingly to ANC and complete blood count (CBC).
Patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation hematopoietic syndrome of acute radiation syndrome: The recommended dose of Filgrastim is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg as a single daily subcutaneous injection for patients exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation.
Patients with HIV infection: The recommended starting dose of Filgrastim is 0.1 MU (1.0 mcg)/kg/day is given daily by subcutaneous injection with titration up to a maximum of 0.4 MU (4 mcg) /kg/day until a normal neutrophil count is reached and can be maintained (ANC > 2.0 x 10 9 /I), Or, as directed by the registered physicians.
Cancer patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation: The recommended dosage of Filgrastim following bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg/day given as an intravenous infusion no longer than 24 hours. Administer the first dose of Filgrastim at least 24 hours after cytotoxic chemotherapy and at least 24 hours after bone marrow transplantation. Dose adjustment should be accordingly to absolute neutrophil count (ANC).
Patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell (PBPC) collection and therapy: The recommended dosage of Filgrastim for the mobilization of autologous PBPC is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg/day given by subcutaneous injection for 5-7 days. Administer Filgrastim for at least 4 days before the first leukapheresis procedure and continue until the last leukapheresis. Discontinue Filgrastim if the white blood cell (WBC) count rises to greater than 100,000/mm³.
Patients with severe chronic neutropenia: The recommended starting dosage in patients with congenital neutropenia is 0.6 MU (6 mcg)/kg as a twice daily subcutaneous injection and with idiopathic or cyclic neutropenia is 0.5 MU (5 mcg)/kg as a single daily subcutaneous injection. Dose adjustment should be accordingly to ANC and complete blood count (CBC).
Patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation hematopoietic syndrome of acute radiation syndrome: The recommended dose of Filgrastim is 1.0 MU (10 mcg)/kg as a single daily subcutaneous injection for patients exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation.
Patients with HIV infection: The recommended starting dose of Filgrastim is 0.1 MU (1.0 mcg)/kg/day is given daily by subcutaneous injection with titration up to a maximum of 0.4 MU (4 mcg) /kg/day until a normal neutrophil count is reached and can be maintained (ANC > 2.0 x 10 9 /I), Or, as directed by the registered physicians.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Interaction
Drug Interactions between Filgrast and other drugs have not been fully evaluated. Drugs which may potentiate the release of neutrophils, such as Lithium should be used with caution.
Contraindications
Filgrastim is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to human granulocyte colony-stimulating factors such as Filgrastim or peg-Filgrastim. With severe congenltal neutropenia (Kostmann's syndrome)
Side Effects
Most common side effects in patients-
- With nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs are pyrexia, pain, rash, cough and dyspnea.
- With AML are pain, epistaxis and rash.
- With nonmyeloid malignancies undergoing myeloablative chemotherapy followed by BMT is rash.
- Undergoing peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization and collection are bone pain, pyrexia and headache.
- With severe chronic neutropenia (SCN) are pain, anemia, epistaxis, diarrhea, hypoesthesia and alopecia.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category C. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised if it is administered to women who are breastfeeding.
Precautions & Warnings
- Filgrast should not be administered within 24 hours before and afier chemotherapy
- The possibility of Filgrast acting as a growth factor for any tumor type cannot be excluded
- To avoid -adverse effects of excessive neutrophils complete blood count is recommended twice per week during treatment
- Filgrast is given by subcutaneous or intravenous infusion as required
- Dilution of Filgrast conc less than 5 mcg/ml is not recommended at any time
- Filgrast may be diluted in 5% dextrose as required
Overdose Effects
The maximum tolerated dose of Filgrast has not been determined. Patients in the BMT studies received up to 13.8 MU(138 mcg)/kg/day without toxic effects.
Therapeutic Class
Haematopoietic Agents
Storage Conditions
Refrigerate at 2-8° C. Protect from light. Do not freeze & avoid shaking.