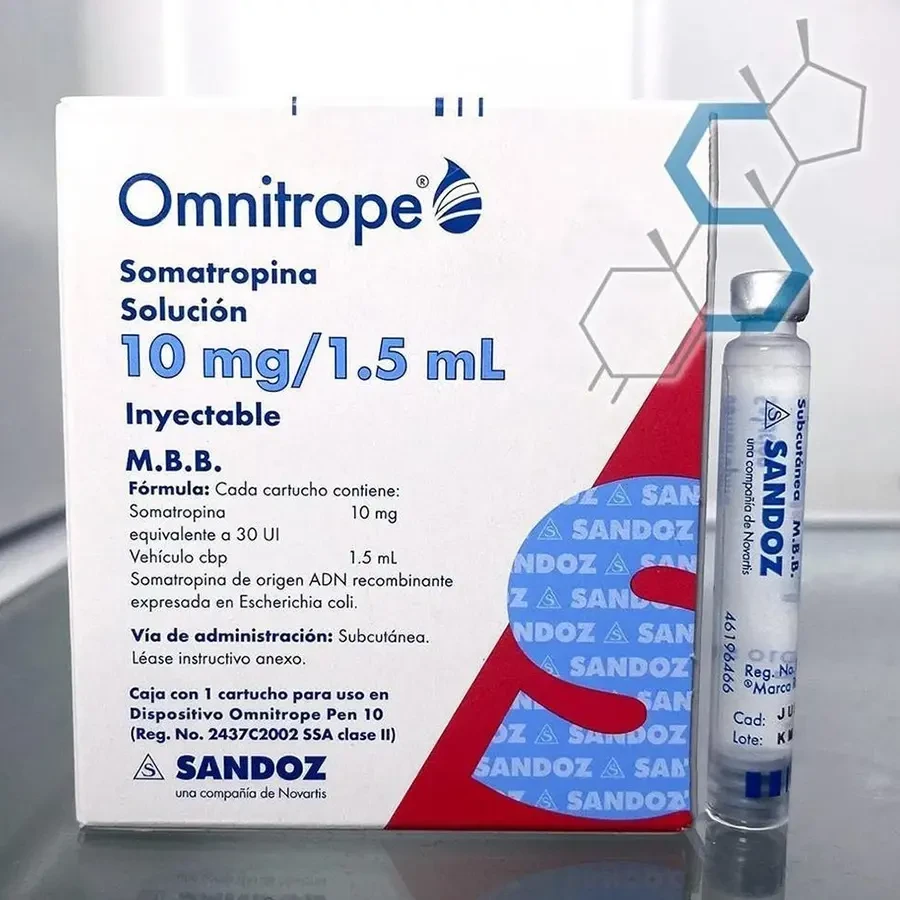
1 Kit Pen:
৳ 20,809.68
This medicine is unavailable
Also available as:
Indications
Pediatric Patients:
- Omnitrope injection is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients with growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH).
- Omnitrope injection is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients with short stature associated with Noonan syndrome.
- Omnitrope injection is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients with short stature associated with Turner syndrome.
- Omnitrope injection is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients with short stature born small for gestational age (SGA) with no catch-up growth by age 2 to 4 years.
- Adult Onset (AO): Patients who have GHD, either alone or associated with multiple hormone deficiencies (hypopituitarism), as a result of pituitary disease, hypothalamic disease, surgery, radiation therapy, or trauma; or
- Childhood-Onset (CO): Patients who were GH deficient during childhood as a result of congenital, genetic, acquired, or idiopathic causes.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Pharmacology
Somatropin (as well as endogenous GH) binds to a dimeric GH receptor in the cell membrane of target cells resulting in intracellular signal transduction and a host of pharmacodynamic effects. Some of these pharmacodynamic effects are primarily mediated by IGF-I produced in the liver and also locally (e.g., skeletal growth, protein synthesis), while others are primarily a consequence of the direct effects of somatropin (e.g., lipolysis).
Dosage & Administration
Somatropin should be administered subcutaneously. Injection sites should always be rotated to avoid lipoatrophy.
- Pediatric growth hormone deficiency: 0.024 to 0.034 mg/kg/day, 6 to 7 times a week.
- Noonan Syndrome: Up to 0.066 mg/kg/day.
- Turner Syndrome: Up to 0.067 mg/kg/day.
- Short stature born small for gestational age (SGA): Up to 0.067 mg/kg/day.
- Adult growth hormone deficiency: 0.004 mg/kg/day to be increased as tolerated to not more than 0.016 mg/kg/day after approximately 6 weeks, or a starting dose of approximately 0.2 mg/day (range, 0.15 to 0.30 mg/day) increased gradually every 1 to 2 months by increments of approximately 0.1 to 0.2 mg/day.
* রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Interaction
- Inhibition of 11ß-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1: May require the initiation of glucocorticoid replacement therapy. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance doses.
- Glucocorticoid Replacement: Should be carefully adjusted.
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Monitor carefully if used with Omnitrope.
- Oral Estrogen: Larger doses of Omnitrope may be required in women.
- Insulin and/or Oral/Injectable Hypoglycemic Agents: May require adjustment.
Contraindications
- Acute Critical Illness
- Children with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese or have severe respiratory impairment-reports of sudden death
- Active Malignancy
- Hypersensitivity to somatropin or excipients
- Active Proliferative or Severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- Children with closed epiphyses
Side Effects
The most common side effects of Omnitrope include headaches, muscle pain, joint stiffness, high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), sugar in your urine (glucosuria).
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Somatropin. It is not known whether Somatropin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Somatropin should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. It is not known whether Somatropin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Somatropin is administered to a nursing woman.
Precautions & Warnings
Acute Critical Illness: Potential benefit of treatment continuation should be weighed against the potential risk
Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children: Evaluate for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment for GHD. Discontinue treatment if these signs occur.
Neoplasm: Monitor patients with preexisting tumors for progression or recurrence. Increased risk of a second neoplasm in childhood cancer survivors treated with Omnitrope- in particular meningiomas in patients treated with radiation to the head for their first neoplasm.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: May be unmasked. Periodically monitor glucose levels in all patients. Doses of concurrent antihyperglycemic drugs in diabetics may require adjustment.
Intracranial Hypertension: Exclude preexisting papilledema. May develop and is usually reversible after discontinuation or dose reduction.
Hypersensitivity: Serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur. In the event of an allergic reaction, seek prompt medical attention.
Fluid Retention (i.e., edema, arthralgia, carpal tunnel syndrome- especially in adults): May occur frequently. Reduce dose as necessary.
Hypoadrenalism: Monitor patients for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases in those with known hypoadrenalism.
Hypothyroidism: May first become evident or worsen.
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: May develop. Evaluate children with the onset of a limp or hip/knee pain.
Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis: May develop.
Pancreatitis: Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain.
Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children: Evaluate for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment for GHD. Discontinue treatment if these signs occur.
Neoplasm: Monitor patients with preexisting tumors for progression or recurrence. Increased risk of a second neoplasm in childhood cancer survivors treated with Omnitrope- in particular meningiomas in patients treated with radiation to the head for their first neoplasm.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: May be unmasked. Periodically monitor glucose levels in all patients. Doses of concurrent antihyperglycemic drugs in diabetics may require adjustment.
Intracranial Hypertension: Exclude preexisting papilledema. May develop and is usually reversible after discontinuation or dose reduction.
Hypersensitivity: Serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur. In the event of an allergic reaction, seek prompt medical attention.
Fluid Retention (i.e., edema, arthralgia, carpal tunnel syndrome- especially in adults): May occur frequently. Reduce dose as necessary.
Hypoadrenalism: Monitor patients for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases in those with known hypoadrenalism.
Hypothyroidism: May first become evident or worsen.
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: May develop. Evaluate children with the onset of a limp or hip/knee pain.
Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis: May develop.
Pancreatitis: Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain.
Therapeutic Class
Drugs for Growth failure
Storage Conditions
Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Avoid direct light. Keep out of reach of children.